Multi-Step Progress Components in React Native
Building Beautiful Multi-Step Progress Components in React Native: A Complete Guide
Creating reusable, customizable stepper components for onboarding flows, checkout processes, and multi-step user experiences
Introduction
In modern mobile applications, multi-step processes are everywhere - from user onboarding to checkout flows, from account setup to complex wizards. A well-designed progress indicator not only helps users understand where they are in a process but also provides visual feedback that keeps them engaged.
In this blog post, I'll walk you through building a comprehensive stepper progress component system for React Native that includes both horizontal and vertical orientations, with full customization capabilities and TypeScript support.
What We're Building
Our stepper component system includes:
- Horizontal Stepper: Perfect for compact layouts and simple progress indication
- Vertical Stepper: Ideal for detailed step information and longer processes
- Full TypeScript Support: Type-safe props and interfaces
- Customizable Styling: Colors, sizes, and visual states
- Production Ready: Clean code, proper error handling, and responsive design
Project Setup
Let's start by setting up our React Native project with Expo:
# Create a new Expo project
npx create-expo-app stepper-progress --template blank-typescript
cd stepper-progress
# Install dependencies
npm install
Core Component Architecture
Step Interface
First, let's define our core data structure:
export interface Step {
label: string;
description?: string;
}
This simple interface allows us to define steps with required labels and optional descriptions, making our components flexible for different use cases.
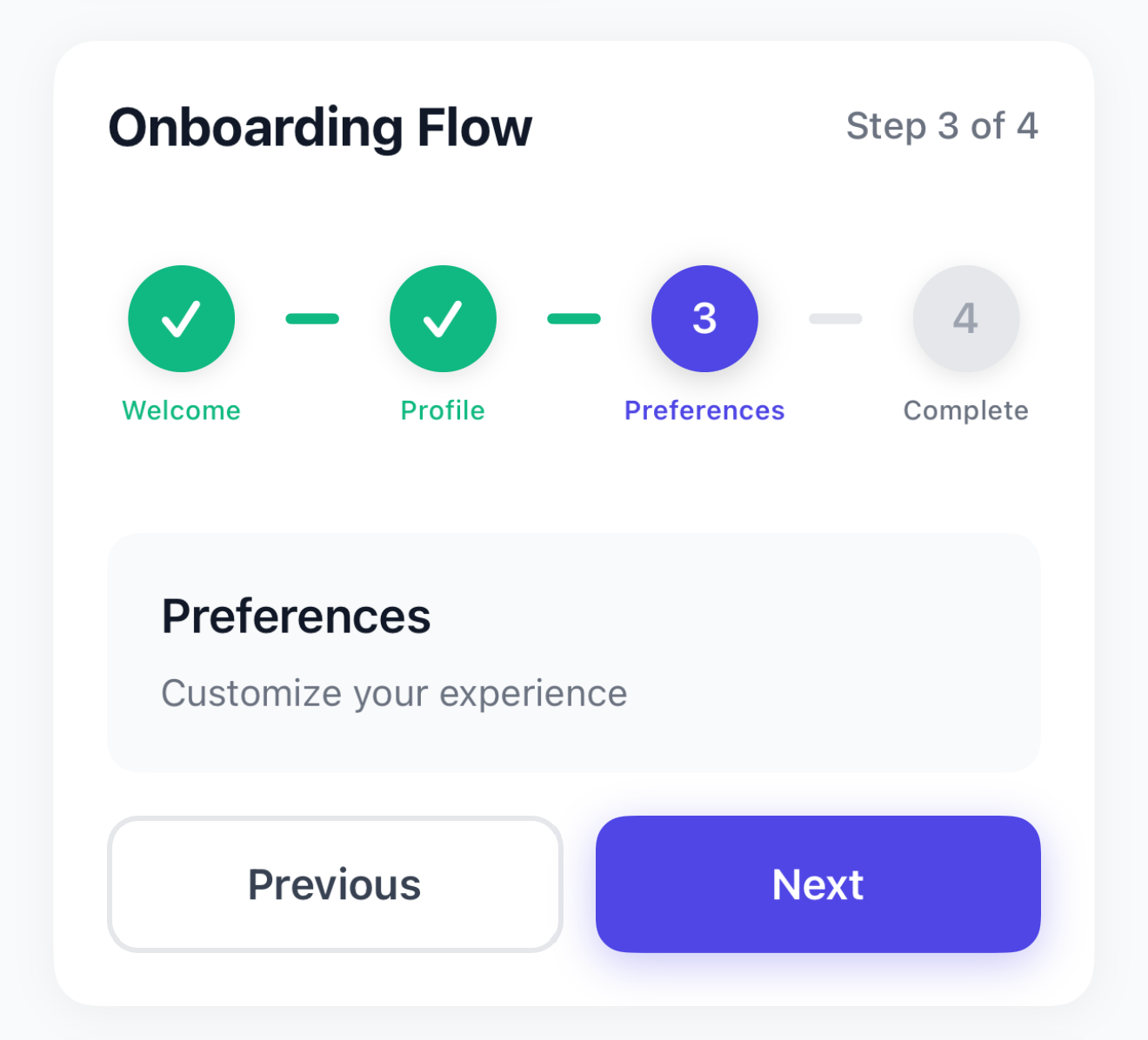
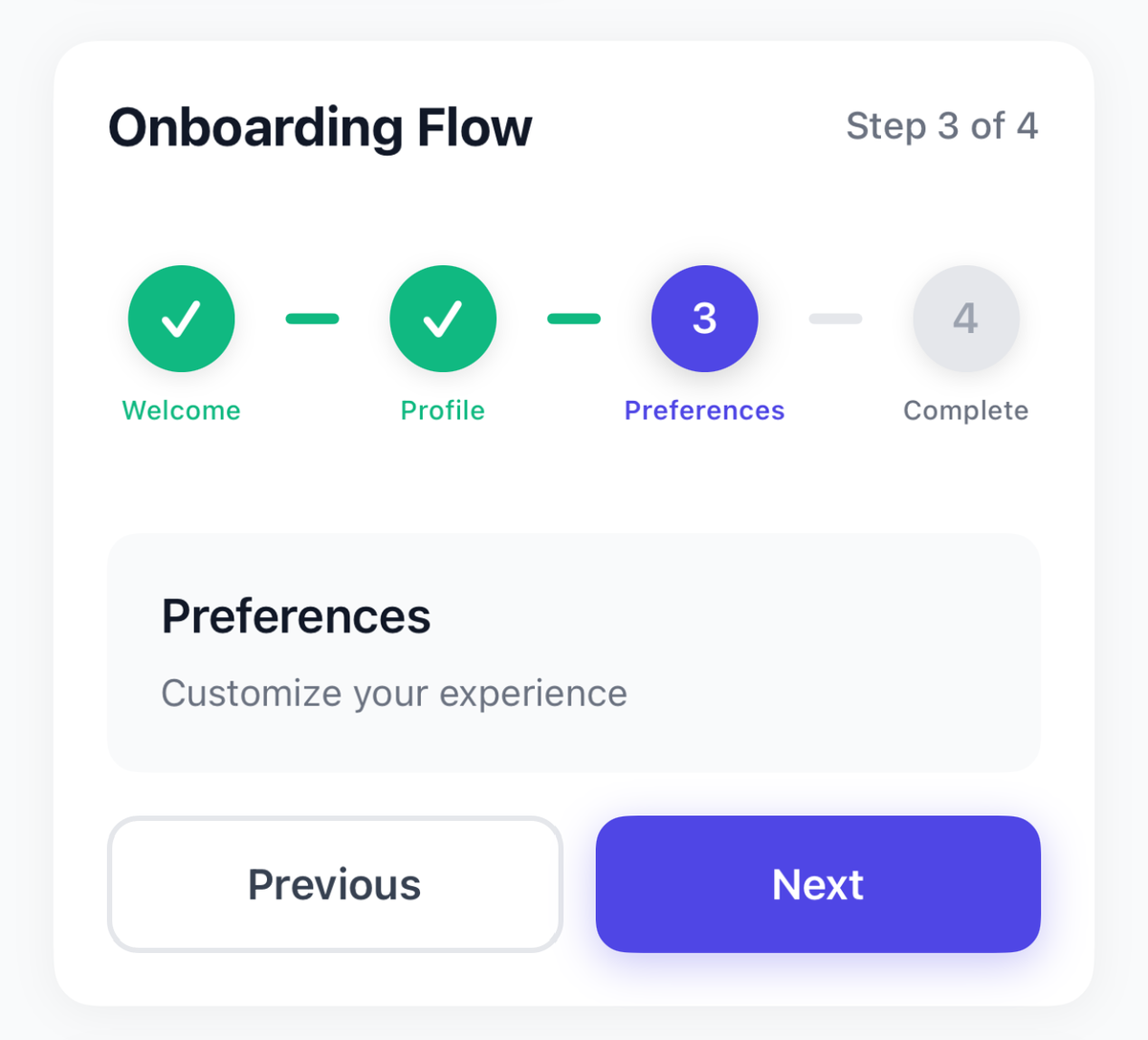
Horizontal Stepper Component
The horizontal stepper is perfect for compact layouts and provides a clean, linear progress indication:
interface StepperProgressProps {
steps: Step[];
currentStep: number;
activeColor?: string;
inactiveColor?: string;
completedColor?: string;
labelStyle?: 'below' | 'inline' | 'none';
showDescription?: boolean;
}
Key Features:
- Circular step indicators with numbers or checkmarks
- Connecting lines between steps
- Color-coded states (active, completed, inactive)
- Optional step labels and descriptions
- Responsive design that adapts to different screen sizes
Visual States:
- Inactive: Gray circles with step numbers
- Active: Colored circle with enhanced shadow
- Completed: Colored circle with checkmark
Vertical Stepper Component
The vertical stepper is ideal for detailed processes where you need more space for step information:
interface VerticalStepperProps {
steps: Step[];
currentStep: number;
activeColor?: string;
inactiveColor?: string;
completedColor?: string;
showDescription?: boolean;
}
Key Features:
- Left-aligned circular indicators
- Vertical connecting lines
- Right-aligned step content
- More space for descriptions
- Better for longer step lists
Implementation Deep Dive
Step Circle Rendering
The core of our stepper is the step circle rendering logic:
const renderStepCircle = (index: number) => {
const isCompleted = index < currentStep;
const isActive = index === currentStep;
const isFuture = index > currentStep;
let circleColor = inactiveColor;
if (isCompleted) circleColor = completedColor;
if (isActive) circleColor = activeColor;
return (
<View style={styles.stepContainer} key={index}>
<View style={styles.stepCircleContainer}>
<View
style={[
styles.stepCircle,
{ backgroundColor: circleColor },
isActive && styles.activeCircle,
]}
>
{isCompleted ? (
<Text style={styles.checkmark}>✓</Text>
) : (
<Text
style={[
styles.stepNumber,
(isActive || isCompleted) && styles.stepNumberActive,
]}
>
{index + 1}
</Text>
)}
</View>
</View>
{/* Label rendering logic */}
</View>
);
};
Connector Rendering
The connectors between steps provide visual continuity:
const renderConnector = (index: number) => {
if (index === steps.length - 1) return null;
const isCompleted = index < currentStep;
const connectorColor = isCompleted ? completedColor : inactiveColor;
return (
<View
key={`connector-${index}`}
style={[
styles.connector,
{ backgroundColor: connectorColor },
]}
/>
);
};
Styling Strategy
Our styling approach focuses on:
- Consistent Spacing: Using consistent margins and padding
- Visual Hierarchy: Different font weights and sizes for different elements
- State Indication: Clear visual differences between states
- Responsive Design: Flexible layouts that work on different screen sizes
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
stepCircle: {
width: 40,
height: 40,
borderRadius: 20,
alignItems: 'center',
justifyContent: 'center',
elevation: 2,
shadowColor: '#000',
shadowOffset: { width: 0, height: 2 },
shadowOpacity: 0.1,
shadowRadius: 4,
},
activeCircle: {
elevation: 4,
shadowOpacity: 0.2,
shadowRadius: 6,
},
// ... more styles
});
Usage Examples
Basic Horizontal Stepper
import StepperProgress from './components/StepperProgress';
const steps = [
{ label: 'Welcome', description: 'Get started with your journey' },
{ label: 'Profile', description: 'Set up your personal information' },
{ label: 'Preferences', description: 'Customize your experience' },
{ label: 'Complete', description: 'You\'re all set!' },
];
<StepperProgress
steps={steps}
currentStep={currentStep}
activeColor="#4F46E5"
completedColor="#10B981"
showDescription={true}
/>
Vertical Stepper with Custom Colors
import VerticalStepper from './components/VerticalStepper';
const checkoutSteps = [
{ label: 'Cart', description: 'Review your items' },
{ label: 'Shipping', description: 'Enter delivery address' },
{ label: 'Payment', description: 'Choose payment method' },
{ label: 'Confirm', description: 'Place your order' },
];
<VerticalStepper
steps={checkoutSteps}
currentStep={checkoutStep}
activeColor="#7C3AED"
completedColor="#059669"
showDescription={true}
/>
Real-World Applications
1. User Onboarding
Perfect for guiding new users through app setup:
const onboardingSteps = [
{ label: 'Welcome', description: 'Get started with your journey' },
{ label: 'Profile', description: 'Set up your personal information' },
{ label: 'Preferences', description: 'Customize your experience' },
{ label: 'Complete', description: 'You\'re all set!' },
];
2. E-commerce Checkout
Streamline the purchase process:
const checkoutSteps = [
{ label: 'Cart', description: 'Review your items' },
{ label: 'Shipping', description: 'Enter delivery address' },
{ label: 'Payment', description: 'Choose payment method' },
{ label: 'Confirm', description: 'Place your order' },
];
3. Account Setup
Guide users through account creation:
const accountSteps = [
{ label: 'Email', description: 'Verify your email address' },
{ label: 'Password', description: 'Create a secure password' },
{ label: 'Profile', description: 'Add your personal details' },
{ label: 'Verification', description: 'Complete identity verification' },
];
Advanced Features
Custom Styling
Both components accept custom colors and can be easily styled:
<StepperProgress
steps={steps}
currentStep={currentStep}
activeColor="#FF6B6B" // Custom active color
completedColor="#4ECDC4" // Custom completed color
inactiveColor="#E0E0E0" // Custom inactive color
showDescription={true}
/>
State Management Integration
The components work seamlessly with any state management solution:
const [currentStep, setCurrentStep] = useState(0);
const handleNext = () => {
if (currentStep < steps.length - 1) {
setCurrentStep(currentStep + 1);
}
};
const handlePrevious = () => {
if (currentStep > 0) {
setCurrentStep(currentStep - 1);
}
};
Best Practices
1. Step Definition
- Keep step labels concise but descriptive
- Use descriptions to provide additional context
- Ensure steps are logically ordered
2. Visual Design
- Use consistent colors throughout your app
- Ensure good contrast for accessibility
- Test on different screen sizes
3. User Experience
- Provide clear navigation controls
- Show progress percentage when helpful
- Allow users to go back to previous steps when appropriate
4. Performance
- Use React.memo for step components if needed
- Avoid unnecessary re-renders
- Optimize images and icons
Testing Your Components
Unit Testing
Test individual component behavior:
import { render } from '@testing-library/react-native';
import StepperProgress from './StepperProgress';
test('renders correct number of steps', () => {
const steps = [
{ label: 'Step 1' },
{ label: 'Step 2' },
{ label: 'Step 3' },
];
const { getByText } = render(
<StepperProgress steps={steps} currentStep={0} />
);
expect(getByText('Step 1')).toBeTruthy();
expect(getByText('Step 2')).toBeTruthy();
expect(getByText('Step 3')).toBeTruthy();
});
Integration Testing
Test complete user flows:
test('navigates through all steps', async () => {
const { getByText } = render(<App />);
// Start at step 1
expect(getByText('Step 1 of 4')).toBeTruthy();
// Navigate to step 2
fireEvent.press(getByText('Next'));
expect(getByText('Step 2 of 4')).toBeTruthy();
// Continue through all steps
// ... additional test steps
});
Accessibility Considerations
Screen Reader Support
- Use proper semantic markup
- Provide meaningful labels
- Announce step changes
Visual Accessibility
- Ensure sufficient color contrast
- Use icons alongside colors
- Provide alternative text
Keyboard Navigation
- Support keyboard navigation
- Provide focus indicators
- Handle keyboard shortcuts
Performance Optimization
Memoization
Use React.memo for expensive components:
const StepCircle = React.memo(({ step, index, isActive, isCompleted }) => {
// Component implementation
});
Lazy Loading
Load step content only when needed:
const StepContent = React.lazy(() => import('./StepContent'));
// Use with Suspense
<Suspense fallback={<LoadingSpinner />}>
<StepContent step={currentStep} />
</Suspense>
Deployment and Distribution
NPM Package
Create a reusable package:
{
"name": "react-native-stepper-progress",
"version": "1.0.0",
"main": "dist/index.js",
"types": "dist/index.d.ts",
"files": ["dist"],
"peerDependencies": {
"react": ">=16.8.0",
"react-native": ">=0.60.0"
}
}
Documentation
- Include comprehensive README
- Provide live examples
- Document all props and methods
- Include TypeScript definitions
Conclusion
Building a comprehensive stepper progress component system for React Native involves careful consideration of design, usability, and technical implementation. The components we've built provide:
- Flexibility: Both horizontal and vertical orientations
- Customization: Extensive styling options
- Type Safety: Full TypeScript support
- Accessibility: Screen reader and keyboard support
- Performance: Optimized rendering and state management
These components can be used in a wide variety of applications, from simple onboarding flows to complex multi-step processes. The key is to understand your users' needs and design the stepper experience accordingly.
Next Steps
- Extend the Components: Add animations, more styling options, or additional features
- Create Variations: Build specialized steppers for specific use cases
- Add Testing: Implement comprehensive test suites
- Optimize Performance: Profile and optimize for better performance
- Share with Community: Publish as an open-source package
Resources
This blog post demonstrates how to build production-ready stepper progress components for React Native. The complete source code is available in the accompanying repository, and you're free to use, modify, and distribute it according to your needs.
Happy coding! 🚀
Need help building your mobile app?
Let's talk about how we can help you design, build, and scale a high-performance React Native app tailored to your users.
Talk to an Expert